Introduction
Solar panels have proved to be a game changer in the way we generate electricity, but still, there might be this burning question for many – How do solar panels actually work? so, sit tight because we have got everything covered. We have explained the science of solar energy in a simple way such that anyone from a 10-year-old student to a 70-year-old person can understand.
What is Solar Energy?
Humans have used Solar energy for a long, long time. The earliest human beings harnessed the solar power for their use case. The only difference is that they were using it for drying food, berries and beans and we use solar energy primarily for producing electricity. Now this statement may not be true always, but mostly yes… we use solar energy majorly for generating electricity.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
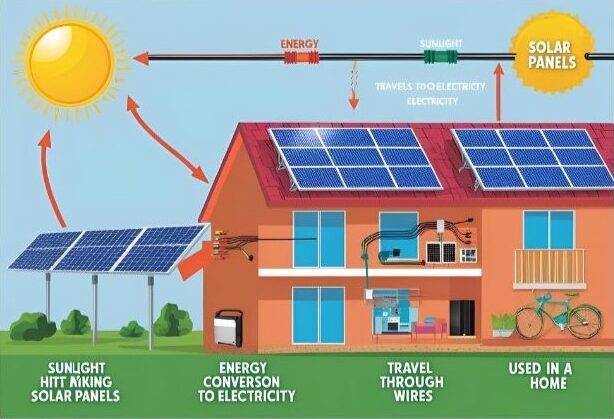
Step 1: Sunlight Falls on the Solar Panel
Manufacturers usually make solar panels from silicon or few other semiconductor material and install them in a metal frame with a glass casing. When photons of sunlight (very small packets/form of energy) hit this material, it releases electrons and produce an electric charge.
Step 2: Creating an Flow of Electricity
Imagine solar panels as a sponge that soaks up sunlight as a sponge soaks water. But a sponge holds the water, however a panel releases energy instead of holding the sunlight. The energy moves within the panel, starting off a reaction that creates an electrical charge.
Step 3: Direct Current (DC) is Produced
The flow of energy that is created on the solar panels is actually a DC (Direct Current) current. DC current is considered to be a stable form of electricity which is mostly produced by sources like batteries. The voltage in a DC circuit hardly changes and remains steady over time, making it ideal for devices that require a stable power supply.
Step 4: Converting the DC to AC
The DC power is not directly usable in most homes because most of the heavy home appliances run on AC power type. A solar inverter works by converting DC (Direct Current) from solar panels into AC (Alternating Current), which can be used in homes.
Inside the inverter, there are electronic components (like transistors and transformers) that switch the DC power rapidly to and fro to create an alternating pattern of waveform. The inverter ensures that the AC generated matches the frequency (50Hz or 60Hz) and voltage (110V or 230V) of the home power supply. This is the most used form of frequency and Voltage combination worldwide.
After conversion, the AC power can be directly used to run appliances like TVs, fans, and refrigerators and if there is excess electricity, it can be stored in a battery.
Simple Analogy:
Think of a solar inverter like a translator.
- The solar panel speaks in DC (one-way flow of electricity).
- The home appliances understand only AC (back-and-forth flow of electricity).
- The inverter translates DC into AC, making the power usable for home appliances.
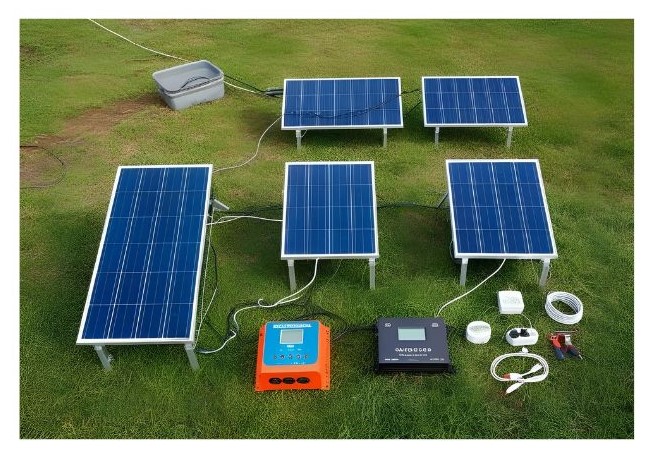
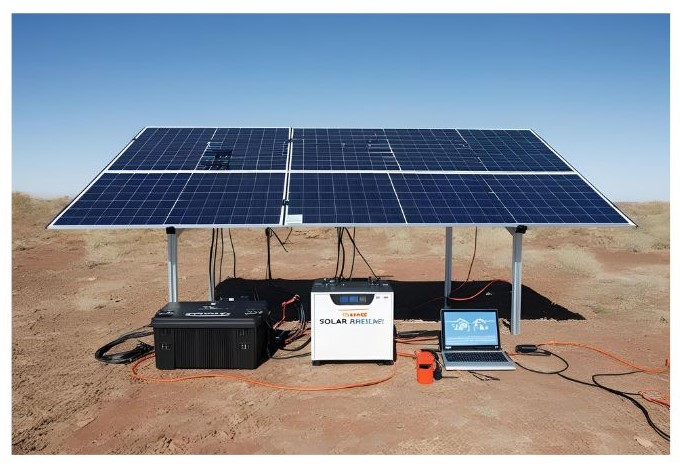
Key Components of a Solar Panel System
1. Solar Panels
These are the main part of the system and absorb sunlight to generate electricity.
2. Inverter
This converts the electricity from DC to AC, making it usable for homes.
3. Battery (Optional)
Suppose your solar panels produce excess amount of electricity than you need, then can store it in a battery and use it as per your requirement or when there’s not abundant sunlight. Especially during night times.
4. Electric Meter and Grid Connection
If your home is connected to the power grid then you can send extra energy to the grid and reduce your electricity bill or you can earn some extra cash by providing some units of electricity to the power company. But this depends on your country/region.
5. Mounting System and Wiring
The angle of placement is very important for installation of the solar panels. A strong and reliable installation also requires high-quality mounting structures. Specialized wiring and junction boxes connect the panels to ensure efficient energy transfer.


Advantages of Solar Energy
Renewable Energy Source: The sun provides infinite energy every day, that too free.
Environment-Friendly: Solar energy is one of best alternatives to fossil fuels. Solar energy reduces carbon emissions and pollution. This helps in fighting climate change and saves environment.
Lower Electricity Bill: As you can generate you’re your electricity there’s no need of thinking about paying your electricity bills.
Low Maintenance: With very minimal servicing and maintenance, solar panels easily can last 20+ years
Scalability: You can expand solar power systems over time, starting with a few panels and adding more as needed.
Common Myths About Solar Panels
Myth: Solar panels don’t work on cloudy days.
Fact: The panels definitely do work on cloudy days, just at a lower efficiency.
Myth: Solar panels need too much maintenance.
Fact: They only need occasional cleaning and last for decades.
Myth: Solar power is too expensive.
Fact: Prices have dropped, and government incentives help reduce costs.
Myth: Solar panels are difficult to install.
Fact: Professional installers handle the setup, and many companies offer hassle-free installation services.
Conclusion
So to sum it up, solar panels are a means to convert sunlight to electricity in a step-by-step process. They absorb sunlight falling on them, convert that energy to a DC current. The inverter converts the DC current into its equivalent usable AC form, allowing it to be directly used in the home. And, batteries store excess AC current for future use.
Ready to Go Solar?
Are you considering installing solar panels? Let us help! Explore a simple guide on solar panel installation in our blog How To Install Solar Panels On Your Roof and take your first step toward a greener future.

